

The 65th '=' symbol is used for padding, since the encoding pulls 6-bit chunks but the data it is usually meant to encode are 8-bit bytes, so sometimes there are only two or 4 bits in the last chunk.
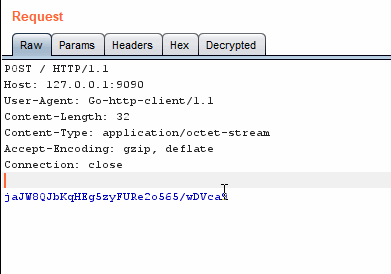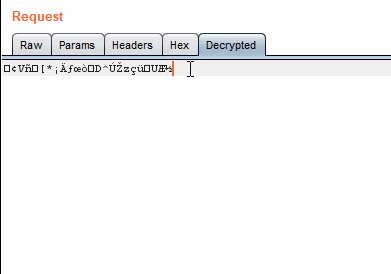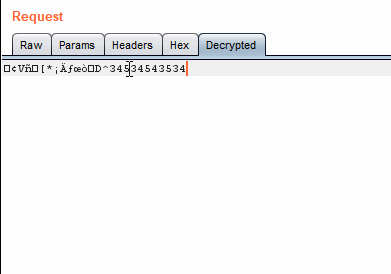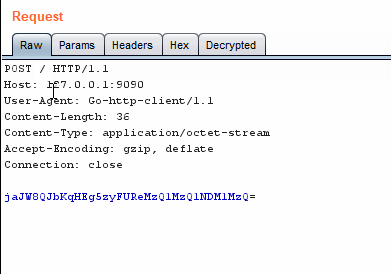
In base64 encoding, the translation is done from left to right those first 64 characters are why it is called base64 encoding. Base-64 in math is a number system like binary or decimal, and you do this change of radix on the entire number, or (if the radix you're converting from is a power of 2 less than 64) in chunks from right to left. This is a character encoding that is based off of the mathematical construct of radix-64 or base-64 number system, but they are very different. Read on for Base-64 stuff.īase64 encoding takes 6-bit binary chunks and encodes them using the characters A-Z, a-z, 0-9, '+', '/', and '=' (some encodings use different characters in place of '+' and '/'). Originally the question title asked about Base-64 encoding. encode() method on it: Python is interpreting the string in utf-8 (the default encoding) and providing you the array of bytes that it corresponds to. That is what is happening when you take a string and call the. The most common (and default in Python 3) is utf-8, especially since it is backwards compatible with ASCII (although, as are most widely-used encodings). You can encode that string (or interpret it) in a variety of ways. In Python 3, str objects are not C-style character arrays (so they are not byte arrays), but rather, they are data structures that do not have any inherent encoding. > data = base64.b64encode(string.encode()) > data = base64.b64encode(b'data to be encoded') You need to push a bytes-like object ( bytes, bytearray, etc) to the base64.b64encode() method. See the Variants summary table at Wikipedia for an overview. In addition, some base64 variants may use characters other than + and /. * Most base64 flavours may also include a = at the end as padding. Which would be the same thing in this case. Or simpler: > encoded = b'data to be encoded' You can convert it to ascii instead, with > encoded = 'data to be encoded'.encode('ascii') In your second example: > encoded = base64.b64encode('data to be encoded')Īll the characters fit neatly into the ASCII character set, and base64 encoding is therefore actually a bit pointless. base64 has no idea what to do with Unicode data, it's not 8-bit. A string is a sequence of Unicode characters. If you remove the b, it becomes a string. You create those in Python 3 with the b'' syntax. Other Base64 variations share the same property but they use different symbols in the last two values.Base64 encoding takes 8-bit binary byte data and encodes it uses only the characters A-Z, a-z, 0-9, +, /* so it can be transmitted over channels that do not preserve all 8-bits of data, such as email. The Base64 implementation in MIME uses a-z, A-Z and 0-9 for the first 62 values. This mixture leaves the data impossible to be altered in transportation thru information systems, such as electronic mail, that were typically not 8-bit clean. The common concept is to select a set of 64 characters that is both part of a subset typical to most encodings.

The specific set of characters chosen for the 64 characters needed for the base can vary among implementations. Base64 is generally used in a number of applications including electronic mail via MIME, and keeping complex information in XML. This guarantees that the data stays unchanged without modification during transfer. Types of URI charactersīase64 encoding schemes are generally used when there is a need to encode binary information that needs to be stored and transferred over media that are developed to deal with textual information. Basically, Base64 is a collection of related encoding designs which represent the binary information in ASCII format by converting it into a base64 representation. The term Base64 is coming from a certain MIME content transfer encoding.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
